
#ACCELERATION OF GRAVITY LAB FREE#
Assuming no air resistance, describe the motion of an object in free fall. A frame-by-frame analysis of the mass in free fall will be used to determine the position of the object at set times. Turn the current to the electromagnet off. The overall aim of the experiment is to calculate the value of the acceleration due to gravity, g This is done by measuring the time it takes for a ball-. Students can achieve increasing levels of accuracy by measuring acceleration with a stopwatch, photogate, and motion sensor. Determine the acceleration due to gravity g using video analysis Introduction In this lab, a mass will be dropped from a height of 2.0 m.Switch on the current to the electromagnet and place the ball-bearing directly underneath so it is attracted to it.Place the cushion directly underneath the end of the glass tube to catch the ball-bearing when it falls through 3.8b for the acceleration, (, we find: ( 2J A', (3.9) 4.Measure this distance between the two light gates as the height, h with a metre ruler.Attach both light gates around the glass tube at a starting distance of around 10 cm.Make sure it faces directly downwards and not at an angle Place the glass tube directly underneath the electromagnet, leaving space for the ball-bearing. Calculate the acceleration of gravity using simple materials, a cell phone, and a computer to record, watch, and analyze the motion of a dropped object.Do not switch on the current till everything is set up This correspond to a relative difference of 22 with the accepted value ( 9.8 m/s 2 ), and our result is not consistent with the accepted value.
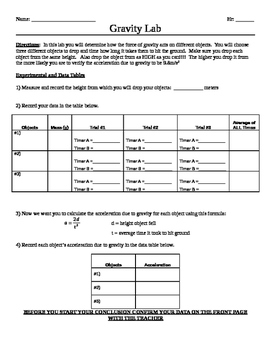
Set up the apparatus by attaching the electromagnet to the top of a tall clamp stand. In this experiment, we measured g by measuring the period of a pendulum of a known length.

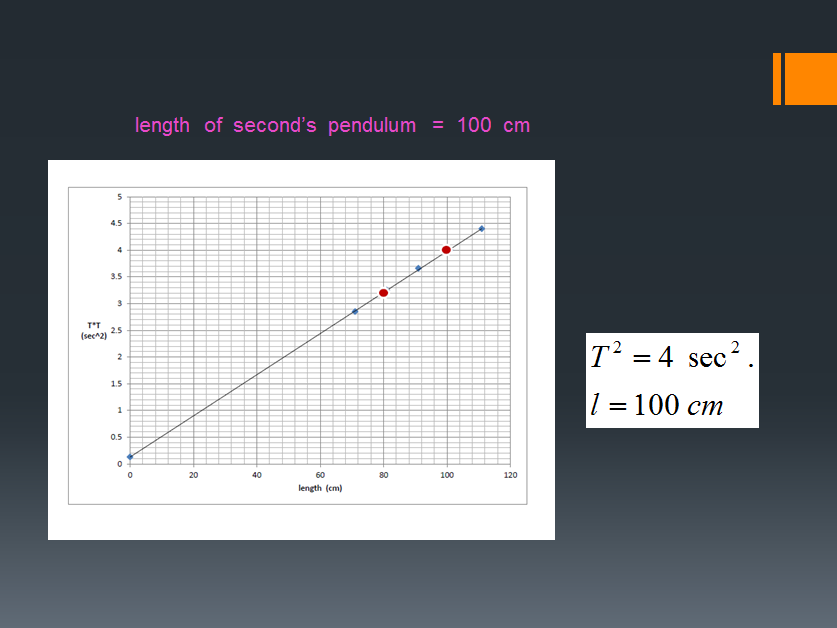
This method is an example of the procedure for varying the height the ball-bearing falls and determining the time taken – this is just one possible relationship that can be tested This component is determined experimentally by measuring the velocity v of the glider after it has accelerated a fixed distance S down the track.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
